Make.com vs n8n: Comparing AI Agent Capabilities in No-Code Automation Tools
AI agents in no-code automation platforms: Make vs n8n. Learn what tool offers better integration, flexibility and value for business automation needs
Last updated: Apr 26, 2025
Table of Contents
📝 Audio Version
Listen to this AI-generated podcast summarizing the article content for easier digestion
Automation tools are evolving rapidly with the integration of AI agents that can perform complex tasks without human intervention. For business and technical teams looking to implement these tools, two platforms stand out: Make.com and n8n. Both offer AI agent capabilities within their no-code automation environments, but they differ in their approach, flexibility, and use cases.
In this comparison, I'll examine the approach of building AI agents on these platforms and the integration with existing systems.
Let's clarify what AI agents are in the context of automation tools before diving in.
AI agents are autonomous software programs powered by large language models (LLMs) that can understand instructions and can decide which actions to perform across various systems. Unlike conventional automation workflows that follow predefined paths, AI agents can:
- Interpret natural language requests
- Access and use different tools and applications
- Make decisions based on available information
- Complete complex tasks with minimal human input
Both Make.com and n8n implement AI agents as entities with a system prompt and connected "tools" that they can invoke to reach specific goals.
Make's approach to AI agents centers around a no-code visual builder with centralized agent management. It's important to note that Make's AI agent feature is currently in beta. It may have some unexpected behaviors – something to consider for production deployments.
On Make, an AI agent is defined as an entity with:
- A system prompt (the agent's "role")
- Connected "tool scenarios" (workflows the agent can run)
- Integration with an LLM provider (like OpenAI)
The platform offers a clean, visual interface for creating and managing agents, with all components centralized within the Make environment.
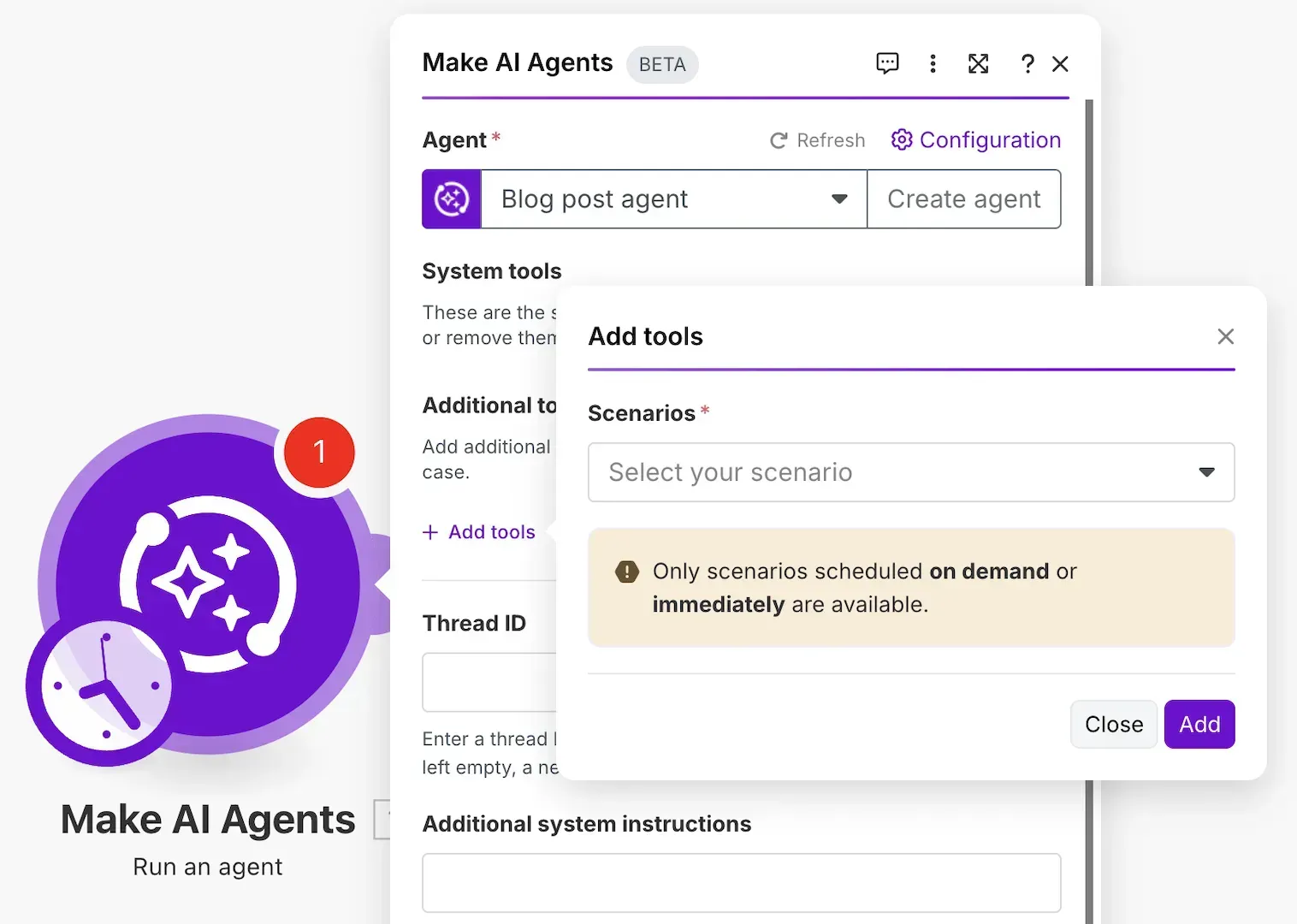
AI agent module in the scenario builder
n8n takes a more modular, open-source approach to AI agents. In n8n, an AI agent is represented as a node within a workflow, with:
- Connection to a model (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.)
- Memory capabilities for context retention
- Tool sub-nodes representing services the agent can access
The platform offers significant flexibility in how agents are configured and deployed.
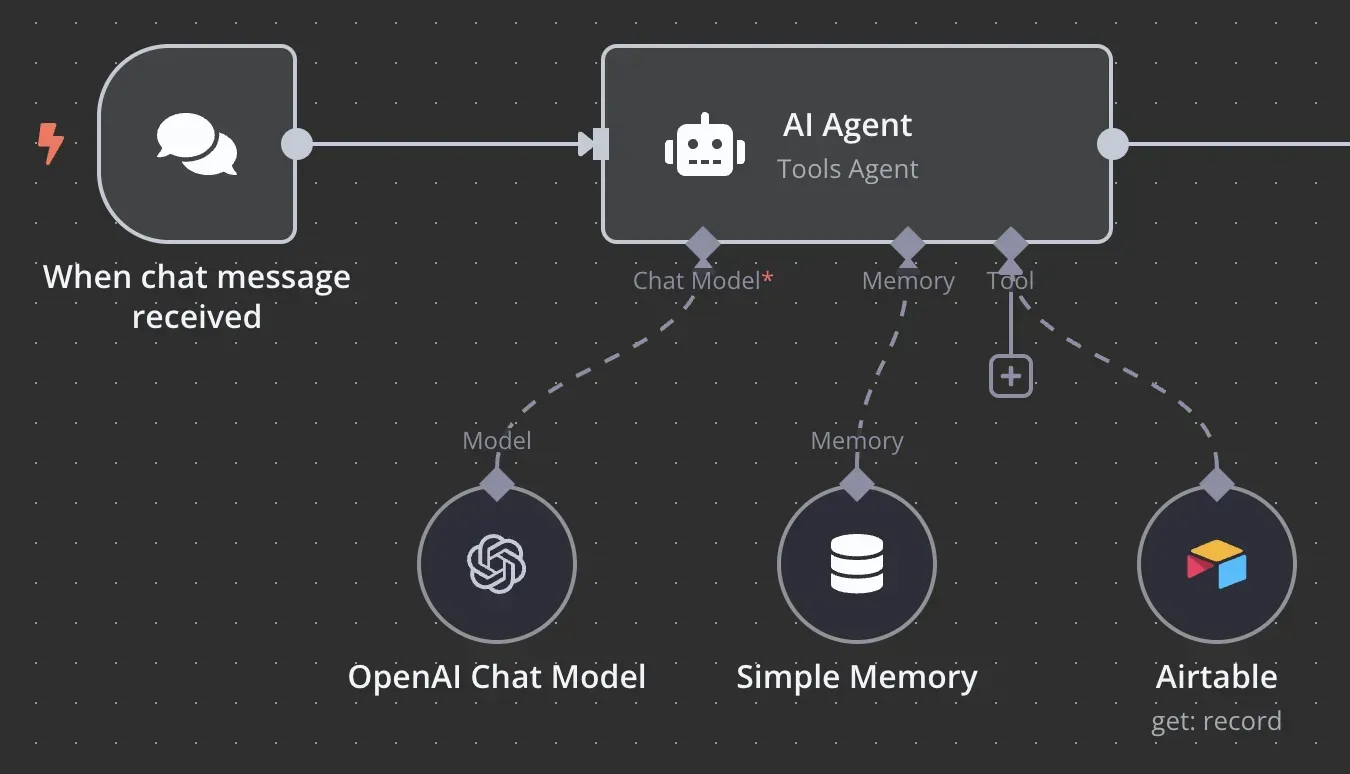
AI agent node in n8n workflow builder
Make.com:
- Navigation to dedicated AI Agents section
- Agent creation with name and role description
- LLM provider connection (OpenAI, Claude, etc.)
- Tool scenarios added as self-contained workflows
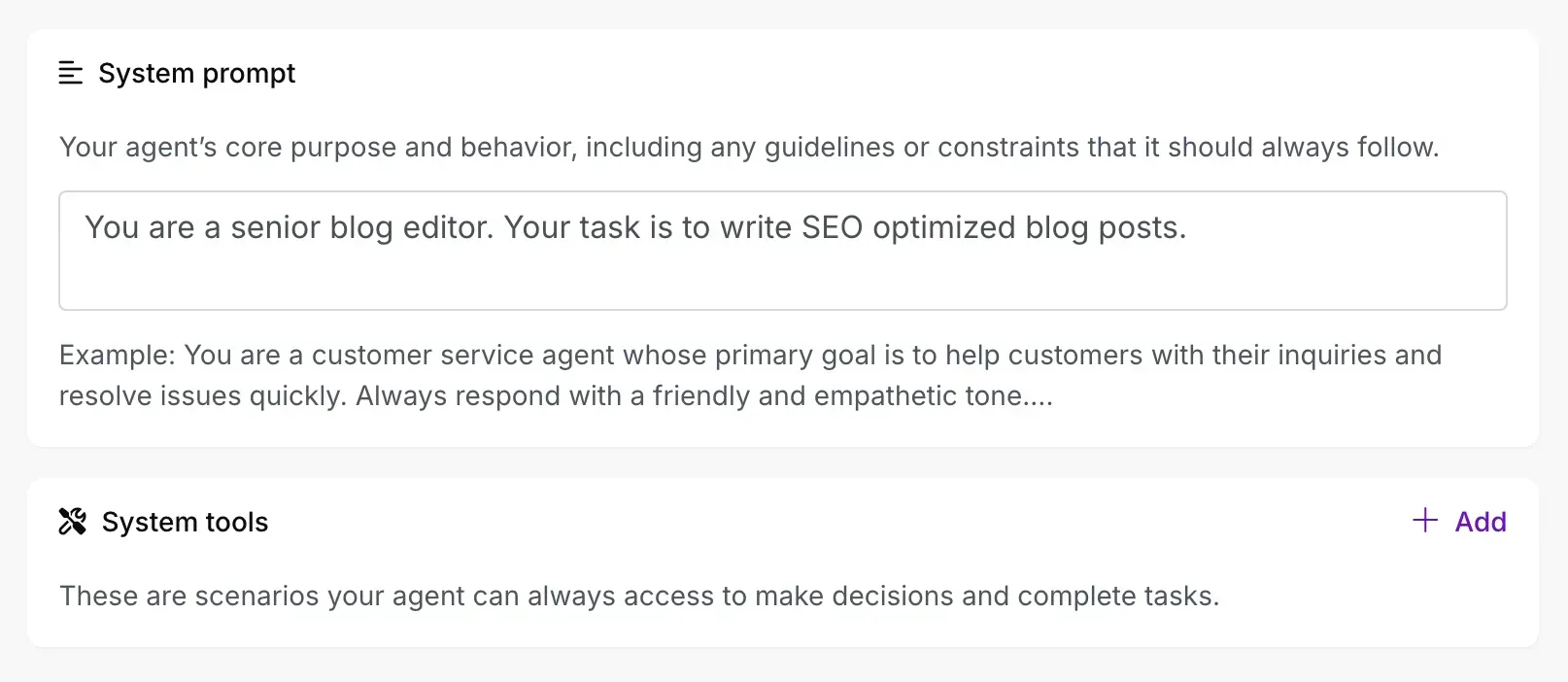
Make AI agent section
n8n:
- AI Agent node placed within a workflow
- Tool sub-nodes attached for each external service
- Model credentials configured directly in the canvas
- Seamless integration with the broader workflow environment
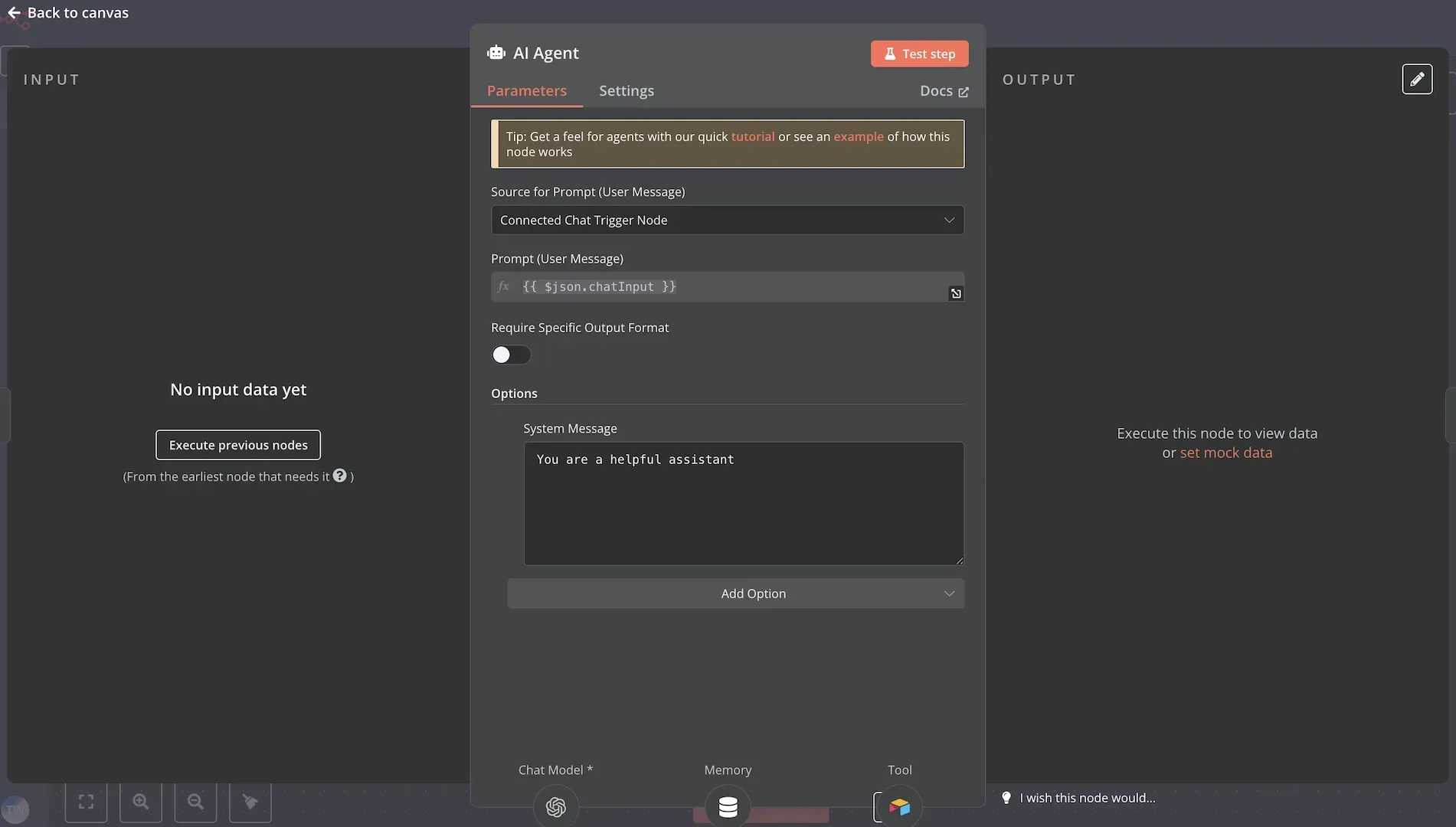
n8n AI agent node settings
Make's approach centralizes agent management in a dedicated section, while n8n integrates agents more deeply into existing workflow structures. This fundamental difference affects how teams organize and maintain their automation ecosystems.
Make.com:
- Over 2,000 standard apps available as tools
- Tools accessed through pre-built scenarios only
- Centralized management of tool connections
- Polished, consistent interface across integrations
n8n:
- 422+ apps and services via LangChain tooling
- Direct connection to apps or other n8n workflows
- Community-curated templates for common use cases
- More flexibility in how tools are accessed and combined
The key distinction here is that Make requires agents to access tools through scenarios you've previously built, while n8n allows connecting apps directly or linking to other workflows, offering more flexibility in implementation.
Make.com:
- Various LLM providers supported (OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Claude)
- API key management centralized per agent
- Uniform agent treatment with no distinct "agent types"
- Streamlined configuration process
n8n:
- Multiple chat models supported (OpenAI, Anthropic, Groq, Mistral Cloud, Azure)
- Enhanced output parsing capabilities
- LangChain-style tool interfaces
- More granular control over agent behavior
n8n leverages its Tools Agent to provide enhanced functionality with various AI models, while Make offers a more standardized approach across different LLM providers.
Make.com:
- Cloud-only operation in Make's environment
- Agents and scenarios managed through web app
- Fully managed infrastructure
- Limited control over data location and processing
n8n:
- Cloud hosting through n8n Cloud (paid plans)
- Self-hosting option with community edition
- Full control over data and infrastructure when self-hosted
- Greater flexibility for compliance and security requirements
This represents one of the most significant differences between the platforms. Make offers a fully managed cloud solution, while n8n provides options for both cloud and self-hosted deployments, giving organizations greater control over their data and infrastructure.
Make.com:
- Plans tiered by operation count
- AI Agents included in paid plans
- Costs scale with usage and scenario runs
- Separate API usage fees for LLM calls
n8n Cloud:
- Starts at $20 per month (annually billed)
- 2,500 executions, unlimited steps, and five active workflows included
- Unlimited self-hosted use at no platform fee
- Separate API usage fees for LLM calls
Both platforms incur additional costs for LLM API usage, typically a few cents per query when using models like OpenAI's GPT-4. The total cost will depend on your implementation and usage patterns.
- Enterprise Environments with Managed SaaS Preferences Make's polished interface and managed cloud environment make it ideal for organizations that prefer not to manage infrastructure.
- Centralized Agent Management Teams looking to maintain a clear overview of all AI agents in one place will appreciate Make's dedicated agent management section.
- Visual-First Automation Design Make's visual canvas provides an intuitive environment for designing complex automation workflows that integrate with AI agents.
- Organizations with Self-Hosting Requirements Compliance-focused or security-conscious organizations that need complete control over their data and infrastructure.
- Advanced LangChain Integration Needs Teams looking to leverage the full capabilities of LangChain for more sophisticated AI agent implementations.
- Open-Source Flexibility Organizations that value the transparency and customization possibilities of open-source solutions.
Choose Make.com if you value:
- A refined no-code builder with visual agent canvas
- Centralized management in a fully managed SaaS
- Streamlined setup and maintenance
- Extensive app integration options (2,000+)
Opt for n8n when you need:
- Open-source flexibility and transparency
- Self-hosting options for data control
- Advanced LangChain integrations
- Customized workflows with granular control
Both platforms dramatically reduce time to market for AI-driven automation and empower technical teams to deliver intelligent solutions. The right choice depends on your specific organizational needs, technical requirements, and preferences regarding hosting and management.
Ready to explore AI agents in automation tools? Here are some recommended next steps:
- Evaluate your hosting requirements - Do you need self-hosting capabilities or is a managed cloud solution sufficient?
- List your essential integrations - Check if both platforms support all the tools and services you need to connect.
- Consider your team's technical expertise - Both platforms are no-code, but n8n may require more technical knowledge for self-hosting scenarios.
- Start with a small automation - Build a simple AI agent on both platforms to test their capabilities with your specific use case.
- Feel free to get in touch. We can discuss which platform might be the best fit for your needs.
This article was based on our "Agents Made Simple" newsletter, helping you stay up-to-date with developments in AI agent technology.
Continuous Improvement
Execution-Focused Guides
Practical frameworks for process optimization: From workflow automation to predictive analytics. Learn how peer organizations achieve efficiency gains through ROI-focused tech adoption.
Explore moreLeave a comment
Your email address won't be published.